What Is Clinical Data Management?



Learn about clinical data management's key role in clinical trials and how technology can improve how that data is connected, prepared, reviewed, and analysed.
Clinical data management (CDM) manages the data protocols for clinical trials, including establishing the right systems, processes, procedures, and training to extract meaningful results and comply with local and federal regulations around the world.
Clinical data management ensures that data collected throughout — and resulting from — a clinical trial is accurate, reliable, and compliant with regulatory standards. It protects the integrity of the trial and lays a foundation on which innovation can begin to take place.
Managing data that arises out of a clinical trial is a big job. The number of data points for just Phase III trials tripled to 3.6 million data points over the course of 10 years. Connecting the dots between all this information and setting up structures that enable researchers to turn them into insights and innovation is at the heart of clinical data management.
You’ll learn:
- Importance of collaboration and coordination in clinical data management
- Roles involved in clinical data management
- Essential skills needed for clinical data management
- How technology is helping streamline clinical data management
- How are emerging technologies driving clinical data management
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Meet Life Sciences Cloud
Get more insights into how Salesforce is helping pharmaceutical companies use artificial intelligence to recruit patients, keep them, and assess results.


Importance of collaboration and coordination in clinical data management
The key players in clinical data management need to work together closely to ensure successful outcomes. This includes the pharmaceutical companies and medical device makers who sponsor trials, the clinical research organisations who often run the trials, and the site personnel who collect and enter data into systems.
The primary objective of clinical data management processes is to provide high-quality data. Effective clinical data management keeps the number of errors and amount of missing data to a minimum. Accessible, high-quality data enables teams, researchers, and organisations to garner insights and draw important analyses. To do this properly, a variety of processes are put in place, namely clinical data management systems with embedded audit trails.
Though the scope of a clinical trial may be broad, the scope of clinical data management is highly defined to a few key tasks. These include:
When done correctly, these tasks set standards for how data is collected, stored, used, and shared. They make sure trials adhere to regulatory statutes and while keeping data and information secure.
The State of Data and Analytics Report
Insights from over 10,000 analytics, IT, and business leaders on data management and decision-making in the age of artificial intelligence.



Implementing advanced analytics tools enables teams to turn complex data sets into meaningful insights with the potential to greatly improve patient outcomes. Organising data and making it accessible also enables organisations and trial teams to provide patients with easy access to their personal health data. This can help keep them engaged and encourage continued participation in the trial.
Despite its large population, India’s contribution to global clinical trials has averaged at 4% per year from 2010 to 2022. Making health data easily accessible through advanced analytics improves transparency and also strengthens patient trust, crucial for maintaining participation in clinical trials in a country like India. In India, some trials have reported retention rates as high as 95–100%, attributed to consistent communication and patient-centric practices.
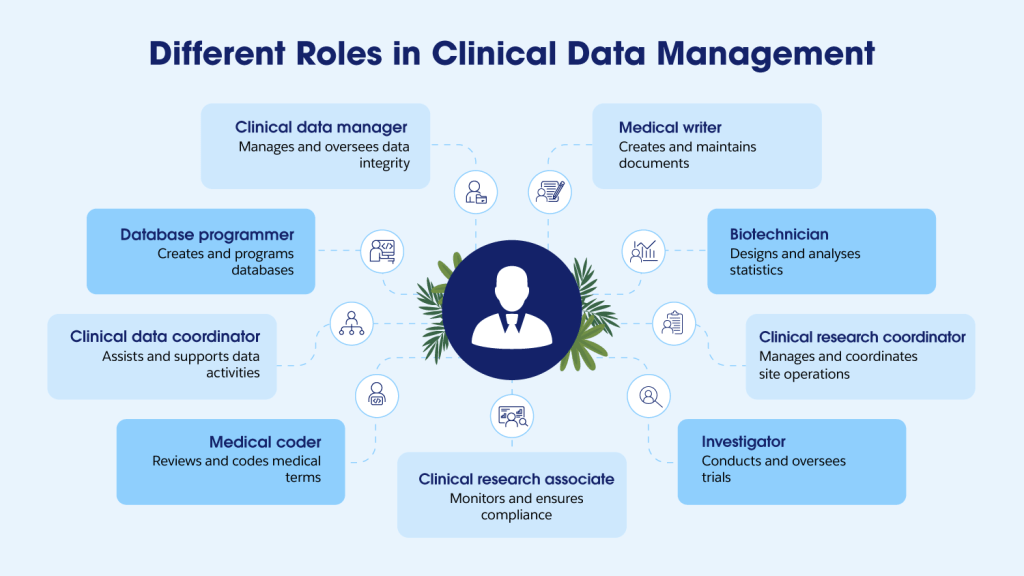
Roles involved in clinical data management
Clinical data management involves a diverse team of specialised professionals, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the success and integrity of clinical trials. From data oversight to regulatory compliance, these roles work collaboratively to maintain the highest standards of clinical research.
Essential skills needed for clinical data management
Clinical data managers have a long list of responsibilities, many of them supervisory. One of their primary responsibilities revolves around designing a data management plan. This plan describes the activities around data acquisition, data review, data cleaning and preparation for data analysis, and submission. These processes make certain that the right data is being collected in the right way, ensuring the study questions can be answered.
Clinical data managers also oversee the creation of a clinical database (alongside database developers and programmers). They have an important role in developing the case report form (CRF) or electronic case report form (eCRF). Sponsors create these forms in conjunction with medical experts, statisticians, and regulatory authorities. Clinical data managers then implement them. The forms define the data fields, specify data types, and outline the units of measurement. They also set the guidelines for form completion. Though CRFs can be paper or electronic, the digital age has pushed heavily toward electronic data collection, pushing for advanced CDMs.
Other responsibilities include managing electronic data, standardising that data, and locking the database at the right moment. They also review data and perform any necessary data cleaning activities.
How technology is helping streamline clinical data management
The pharmaceutical industry, and clinical trials in particular, notoriously struggle to manage data. This makes it hard to connect the dots and requires dedicated staff with the right expertise to manage it. However, even with such expertise, manual data management can present a huge challenge.
With so many moving parts, sponsors need a way to centralise data in one place. CDMs would allow them to collect, monitor, review, and clean data more easily, making it ready to analyse and submit. It would also enable them to automate data collection, organise that data , and gain insights in real-time. These capabilities will become even more important as clinical trials become more complex and the industry moves toward decentralised trials, which require more sophisticated monitoring.
Organisations understand the inherent data management challenges, with many turning to clinical data management tools to help streamline processes, minimise errors, and centralise data collection and related activities. These data management systems not only create the single source of truth, but they also provide an audit trail. When it comes time to submitting the data and results to the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) for approval (in what can be a labour-intensive process), the audit trail can save time and resources.
While powerful on their own, integrating data management systems with other systems can deliver a variety of benefits across a pharmaceutical organisation. It makes it possible for teams to benefit from associated technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and automation that can deliver insights and flag things like quality issues that may occur with the data.
These integrated approaches are becoming increasingly common as organisations recognise the value of connected digital ecosystems in streamlining clinical operations and improving data quality.
How are emerging technologies driving clinical data management
According to recent statistics by MarketsandMarkets, the global clinical data management services market is projected to reach ₹6.11 lakh crore by 2028, indicating a substantial growth trajectory. This growth is fueled by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the number of clinical trials globally.
The volume and complexity of data generated in clinical trials has grown exponentially in recent years. Especially with the rise of decentralised trials, clinical data managers face an unprecedented influx of different data types from multiple sources. It’s becoming more and more difficult to maintain data quality and ensure regulatory compliance due to this surge.
As with many other industries, professionals in clinical data management are looking to use AI to gain better insights into trials. This will require careful data governance to assure that data is HIPAA-compliant, secure, and in the right format for AI. This convergence of data and AI holds great potential for the health and life sciences industries. It spurs innovation, leads to better outcomes, and improves patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A Clinical Data Management System (CDMS) is a specialised software tool designed to handle the data from clinical trials and studies. It’s a crucial part of clinical research, helping to ensure that data is accurate, managed efficiently, and meets all regulatory requirements. CDMS software simplifies the process of collecting, storing, validating, and reporting data from various sources involved in the trial or study.
CDM forms the backbone of credible clinical research in India. It ensures that clinical trials meet the stringent data quality standards required by the regulatory authorities and international best practices. Robust CDM practices help research organisations avoid expensive trial failures, streamline the approval process, and most importantly, safeguard participant wellbeing through precise data management and monitoring throughout the study lifecycle.
Clinical data management consists of 3 stages:
- Start-up – This is the first stage and involves planning and preparation for the clinical trial data management setup. It consists of various activities, some of which include:
- Protocol interpretation review
- Data Management Plan (DMP) development
- Design and develop Case Report Forms (CRF)
- Database design and development
- Database testing
- User acceptance testing
- Conduct – The main focus is on making sure the data is always correct and being watched to support the study results and regulatory requirements. The conduct phase of clinical data management involves:
- Data collection and entry
- Data cleaning and validation
- Close out – This gets triggered with the last patient’s last visit and involves several key activities that aim at ensuring the completeness, accuracy and integrity of the collected data. It consists of activities like:
- Database quality control
- Medical coding review and approval
- SAE reconciliation and approval
- Database lock activities
- Data archiving
- Systematic decommissioning






