With over 8.5 billion searches performed on Google globally each and every day, your pool of potential customers is massive. It’s no surprise, then, that you need to make sure your content ranks high in Google and reaches the people most likely to take an action with your brand.
That’s where doing keyword research, and choosing the right SEO keyword, comes in. It’s an art and a science. As a search engine optimization (SEO) marketing manager at Salesforce, I know what works, and how to get eyeballs on your content.
Let’s say you’ve been tasked with writing a page around “customer service.” Since it’s a broad and often complex topic, you might think that a long-form guide would be the best type of content.
But how do you know for sure? Are you certain there are enough potential customers searching for this term? Is the audience large enough to justify creating the page? Are searchers even looking for long form content on this topic? Are they using the same terms to search for content? Do you know what kind of content Google is ranking for your target term?
Proper keyword research can answer these questions and help you create content that’s user-focused and SEO optimized. Follow these six steps to develop better content, and get better search results.
1. Verify search volume
Start by entering your topic or keyword idea into a SEO research tool such as BrightEdge or SEMRush. These paid tools show the average monthly search volume for your keywords. When verifying keyword search volume, look for terms with an average monthly search volume of 100 searches or greater. However, keep in mind that terms with the highest monthly search volume may not be the most relevant or focused terms to target. You should research and explore all options to find the term with the highest volume and most relevant search results.
2. Research related terms
Always ensure that the term you are targeting is the same your audience is using to find content. SEO keyword research tools can help you identify similar or semantically related terms to see if there is greater search volume with another keyword variant. For example, “customer service best practices” returns 590 monthly searches versus “service best practices” with only 30.
Additionally, using related terms throughout the copy in addition to your target keyword can help your SEO rank by preventing keyword spamming or stuffing. Remember to write naturally, so Google does not penalize your SEO efforts by hurting your ability to rank well on the first page. Don’t feel that you need to cram the keyword into every other sentence. Google itself warns against it with this example: “We sell custom cigar humidors. Our custom cigar humidors are handmade. If you’re thinking of buying a customer cigar humidor, please contact…” You get the idea. Not only is it open to penalization by Google — and less likely to be discovered by searchers — it’s a bad experience for the reader.
3. Explore long-tail keywords
Longer, more specific keywords often indicate searchers who are closer to taking an action. The specificity of the search lets you know they have a specific need or problem. While these terms may have lower search volume than their broader counterparts, they will often lead to more qualified conversions. For example: “customer service” vs. “customer service best practices” or “what is customer service?”
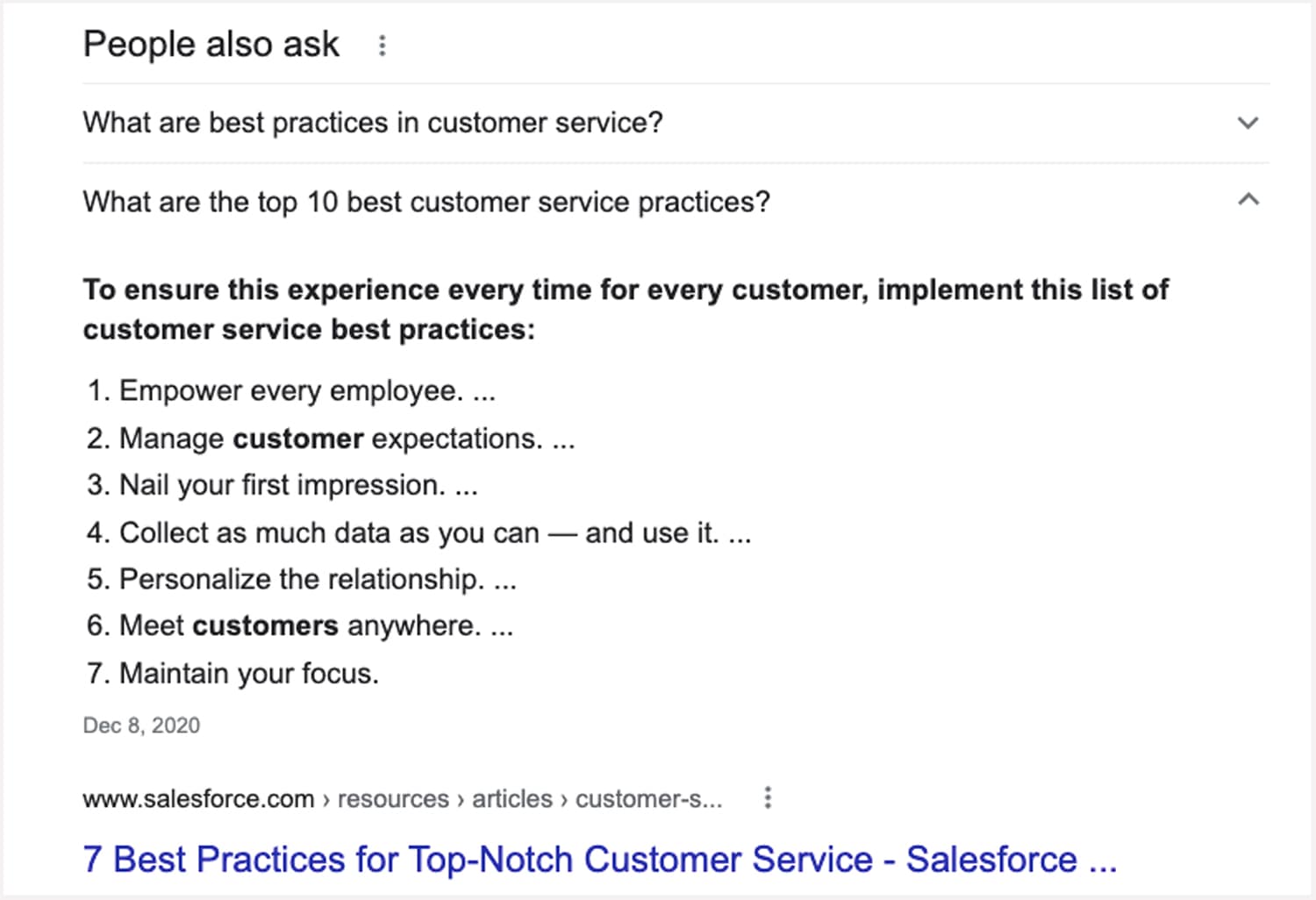
Additionally, some of these longer tail keywords may help land you in one of the coveted “People also ask” answer boxes in Google, especially if used in the page title or a sub-heading.
Google search “People also ask” example:
4. Beyond keyword research: Identify search intent
So you’ve found a high volume, relevant keyword. But do you know what types of content Google is presenting on the first page? Based on your keyword research, what types of content are searchers looking for? Do they want guidance, how-to articles, a list of nearby shops, or something else completely?
To quickly check, we recommend opening an incognito browser window and searching your keyword to see what Google reveals on the first page. You’ll want to open an incognito or private browsing window so your previous searches and browser cookies don’t influence the presented search results. Based on what’s ranking, will your page topic address the same first page search intent?
In the example below, you’ll see that most of the top ranking first page content around the term “customer service best practices” is in listicle format (i.e. “X Best Practices for Customer Service…”). Given these results, it’s best to target your topic in a similar way to increase your chances of ranking on page one.
Search intent example:

5. Study your competition
Are any of your competitors ranking on the first page? If so, what terms are they targeting? What types of content are they creating? How long is their content? What makes them successful? Identifying this will help inform the content strategy for your page, and give you an opportunity to expand on their success.
6. Don’t cannibalize yourself
Always ensure that there are no existing web pages on your own site ranking for or targeted to your selected SEO keyword. Check with your internal SEO team to confirm, or if that’s not an option, perform a site search on Google by typing site:[your website domain] [search query/keyword]. This will bring up a list of pages currently on your site with the target keyword in the copy.
If you find a page targeting the same term, you should determine if that page should be optimized further or removed. Before removing any pages, work with your analytics or marketing team to identify the business impact of removing a page. This could consist of traffic loss or a drop in form completes and leads. If you must remove an existing page, always use a 301 redirect to automatically send the searcher to the newly created page. These redirects pass more of the SEO page equity from the page being redirected to the new page.
If you follow these tips you’ll be on your way to finding the right keywords for SEO and creating targeted, meaningful content which searchers are looking for and need.
Want a deeper dive on keyword research? Check out our SEO Best Practices blog for more guidance on how to write and optimize SEO content for your site.
























