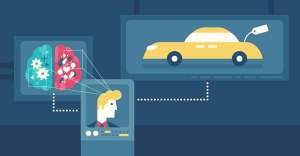
The common theory is that people are driven by one side of their brain: the left side, which is considered logical and analytical, or the right side, said to be intuitive and subjective. No matter which dominates a buyer’s behaviours, both matter when it comes to purchasing decisions.
Customers make choices about what to buy based on motivation and need. The more basic the need, for example, the greater the motivation your customers will have to fulfill it. Your marketing needs to tap into these basic psychological principles in order to cut through the noise, resist distortion, and increase retention. One of the best methods of effective marketing (and business) is to make it all about the buyer.
Make sure the buyer knows what they’ll gain when they purchase your products or services. Stroke their ego, show them the value they’ll get, and make sure they know how their peers (and those they look up to) have bought and benefited from your company. Take into consideration the four main types of factors influencing your customers’ behaviours: cultural, social, personal, and psychological. Learn more about the psychology behind your customers’ behaviours in this infographic.
How to Use Psychology to Predict Your Buyer’s Behaviours
- The brain has two sides and people often describe themselves as either
- Left-brained: logical and analytical
- Right-brained: intuitive and subjective
- Even if a person leans one way, both sides matter during thought processes and purchase decisions
- An example situation: Purchasing a car
- Buyer might have seen a photo [right brain] that pulls them in
- They will then justify the decision to buy by looking up mechanical specifications [left brain]
- Both sides of the brain work to make a purchase decision
- The logical side of buyers relates to facts and figures
- This is why numbers (price, technical specifications) are featured prominently in brochures
- The psychological side of buyers relate to visual components and stories of past successes
- Motivation and Need
- The more basic the need, the greater the motivation consumers have to fulfill it
- Perception, Attention, Distortion, and Retention
- The way the human mind views the world forms the basis of perception
- To get attention, you can use:
- Shock tactics
- Surprise
- Humor
- Get customers to remember your message without letting it get distorted through their outlooks and mindsets
- Repetition helps consumers retain your message
- Learning and Conditioning
- Consumers gain decision-making information from advertising
- If a consumer’s post-purchase experience is negative, they learn to avoid that product (even if the product improves)
- Advertisers then have to teach consumers another message about the product
- The message should remove prior conditioning in favor of new information
- Beliefs and Attitudes
- What consumers believe about a seller, product, or service affects what they buy
- Attitudes can persist even when there are changes to the seller, product, or service
- Advertising strives to position products so they look like they are associated with positive traits
The Basics
- Ego
- Buyers naturally think about themselves and what they stand to gain by making a purchase
- The seller needs to stroke this ego to make the buyer more comfortable with the purchase decision
- Answer this question from their perspective: “What’s in it for me?”
- When you find an answer, you’re one step closer to completing the sale
- Value
- Buyers like the prospect of winning the battle against the seller by getting as much value as possible
- Value is not a fixed number, it’s relative
- It depends on what the buyer has to gain and what they’re willing to pay
- Appeal to buyers’ need to “win” by demonstrating the greatest value possible, relative to the price
- Herd mentality
- Buyers, and humans for that matter, move together in large groups
- They are swayed by what peers do
- Demonstrate to potential buyer how others have bought and benefited
It’s All About the Buyer
- 1. Cultural factors– Different components related to the culture or cultural environment the consumer belongs to
- Sellers need to understand the cultural factors inherent to each market or situation so that product can be adapted
- Example: McDonalds varies it’s product by culture
- France: McBaguette
- India: Chicken Maraja Mac and Masala Grilled Chicken
- Japan: Mega Teriyaki Burger
- Arabic and Muslim countries: Ingredients are all certified halal
- Example: McDonalds varies it’s product by culture
- Sellers need to understand the cultural factors inherent to each market or situation so that product can be adapted
- 2. Social Factors– Significantly influence behavior and fall into three categories; reference groups, family, and social roles and status
- Reference groups
- Social groups to which an individual belongs and are influenced by
- Family
- Perceptions and family habits have a strong influence on consumer buying behavior
- Important for brands to be seen as a family brand in order to become a consumer habit for parents and children
- Social roles and status
- Position of individual with family, work, and friends
- 3. Personal factors– Decisions and buying behavior are influenced by the characteristics of each consumer
- Purchasing power of an individual influences behavior and purchasing decisions
- Affects what they can afford
- Plays a role in the retailers visited
- Can determine social value of product
- Purchasing power of an individual influences behavior and purchasing decisions
- 4. Psychological factors– Divided into 4 categories: motivation, perception, learning, beliefs/attitude
- Motivation
- Drives consumers to develop purchasing behavior
- Brands should try to reinforce a need in the consumer’s mind so they develop a purchase motivation
- Perception
- Process through which an individual selects, organizes, and interprets information
- Attention level varies depending on activity of the individual and number of stimuli in the environment
- Learning
- Changes the behavior of an individual as information and experiences are acquired
- If a good experience is had with a product the consumer will be more likely to buy it again
- Beliefs and attitudes
- A belief is a conviction that an individual has on something based on experiences, learning, and external influences
- An attitude is the predisposition to act a certain way towards an object
- Beliefs and attitudes are part of a person personality
4 Main Types of Factors Influencing Consumer Behaviour
Conclusion
While there is a wide range of behavioral traits that influence purchasing decisions, buyers exhibit many of the same ones. Understanding buyers’ behaviors can help you close more sales and improve your relationship with your consumers.