Building secure AI agents requires more than tools — it demands precision in applying them within real-world workflows. In Part 2 of our Agentforce security series, we turn theory into practice, exploring how to operationalize safeguards that protect workflows from risk.
From the principle of least privilege and secure actions to real-time monitoring and testing, these best practices help organizations confidently deploy secure AI agents that perform reliably and stay within defined boundaries.
Are you new to this series? Start with Part 1 to learn about the five foundational attributes of secure Agentforce implementation.
Zero trust and least privilege
Agentforce, the agentic layer of the Salesforce Platform for deploying autonomous AI agents across any business function, is built to align with Zero Trust principles, which assume no user or system should be trusted by default, even inside the network perimeter. One of the most effective ways to enforce Zero Trust in workflows is by applying the principle of least privilege.
In Agentforce, every agent is associated with a “running user,” an identity that determines what the agent can access and perform. Actions inherit permissions from referenced Apex, Flow, or Prompt Templates. By default, new agents have no permissions, ensuring they only gain access to what is explicitly granted. For example, if an agent identifies users by email, someone could enter another person’s address to access restricted information, a reminder of how GenAI systems can be misused without proper checks. Designing for least privilege reduces the blast radius of agent misuse or misconfiguration and keeps access tightly scoped to what’s necessary.
Best practices
- Start with a minimum access profile.
- Only grant permissions that are essential for the agent’s function.
- Regularly review Role Hierarchy and Organization-Wide Defaults — they can unintentionally expand access.
Access controls
Strong access controls ensure only the right users can trigger sensitive actions, a core requirement for GenAI security, where agents may operate autonomously on high-impact tasks. Because AI agents often act outside direct user sessions, robust identity verification becomes essential, particularly for actions involving sensitive data or system changes.
Best practices
- Require authentication or identity checks for all user-triggered interactions.
- Enforce strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Use step-up authentication (for example, OTP or biometric verification) for sensitive tasks like password resets or profile updates.
Designing secure actions
Actions define what an AI agent can do — retrieving data, initiating workflows, updating records, and more. Without clearly defined boundaries, these actions could be exploited to expose data or trigger unauthorized behavior. Designing secure actions ensures AI agents operate within appropriate limits.
Key design considerations include:
- Scope Limitation: Define boundaries to prevent excessive data access.
- Input Validation: Sanitize both direct user inputs and referenced data.
- Error Handling: Ensure failed actions don’t expose sensitive information.
To further strengthen secure action design, Agentforce also provides a suite of advanced Trust Features to offer administrators greater precision and control over how and when agents perform secure tasks in real time.
- Agent Variables: Session-scoped values used to store verified information during an interaction. These are set only by trusted system actions and cannot be changed by the user.
- Action Bindings: Secure connections between one action into the inputs of another, preventing unauthorized data injection.
- Filtering Rules: Conditional logic expressions used to show or hide topics and actions based on the current session state or verification status until trust conditions are met.
For example, a refund request topic can remain hidden until the user completes identity verification, ensuring that sensitive actions are only available within fully trusted sessions.
Together, these Trust Features allow organizations to design highly secure, context-aware actions that adapt dynamically based on user trust level.
Best practices
- Narrow the scope to limit unnecessary access.
- Integrate identity and permission checks into all private actions.
- Validate and sanitize all inputs to prevent malicious requests.
- Handle errors gracefully to avoid exposing system details or data.
- Leverage Trust Features to dynamically enforce access based on session security.
Monitoring
Monitoring enforces Agentforce security at runtime by giving teams real-time visibility into agent behavior, permissions, and system interactions. Logging conversations, tracking access, and auditing activity help ensure agents operate within defined security boundaries, reinforcing your GenAI security posture.
Best practices
- Review audit trails and access logs regularly to detect suspicious activity.
- Conduct periodic reviews of agent permissions and scope.
- Enable “Enrich event logs with conversation data” in development to store full transcripts for audit and debugging.
- Important: Disable this feature in production to protect sensitive data. When turned off, logs will display “Sensitive data not available.”
Runtime guardrails
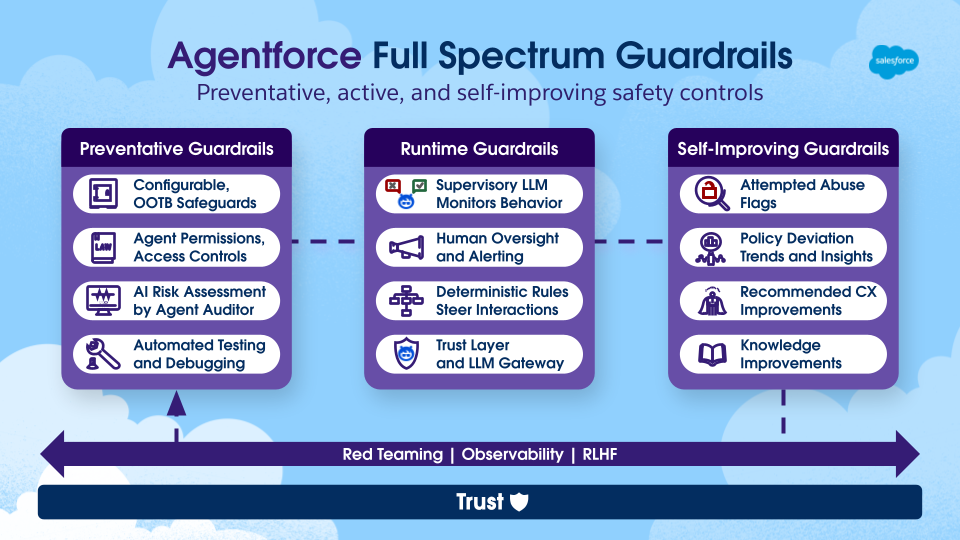
Runtime guardrails monitor live agent interactions for policy violations, unsafe outputs, and inconsistent behavior, helping contain risks in real time.
Agentforce evaluates runtime signals such as:
- Instruction adherence
- Groundedness
- Completeness
- Coherence
Based on these checks, the agent can:
- Escalate suspicious requests
- Regenerate incomplete responses
- Prompt users for clarification
Best practice
- Monitor runtime guardrail activity to proactively manage risky interactions and strengthen agent instructions over time.
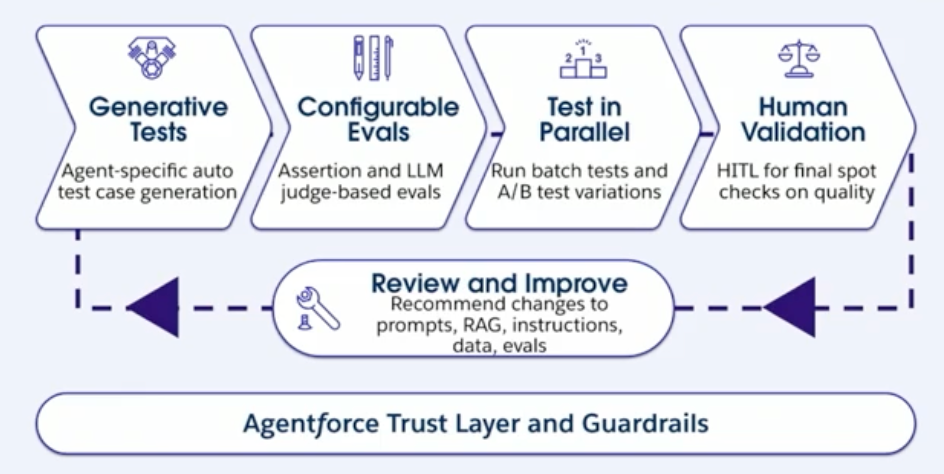
Comprehensive testing
Like any software component, secure AI agents require rigorous testing before deployment. The Agentforce Testing Center offers a low-code framework for simulating, evaluating, and improving agent behavior before deployment.
Testing tools include:
- AI-generated test cases
- Automated evaluation of results
- Human review and approval workflows
Best practices
- Use AI-generated test cases to cover a wide range of scenarios.
- Automate evaluation to speed up quality assurance.
- Conduct a human review before deploying agents in production.
Security is a shared responsibility
Agentic AI security isn’t a one-time setup — it’s an ongoing commitment. While Salesforce delivers the tools and infrastructure, your teams play a critical role in ensuring secure implementation. Agentforce security is most effective when teams actively apply and evolve best practices across identity, permissions, monitoring, and governance — not just during setup, but throughout the life of your AI strategy.
Salesforce’s security resources



Learn more: